
Calculate the total fees paid to the fund managers. The performance of the hedge fund is provided below. Incentive fees are calculated on gross gains and not gains net of management fees. The fund follows a “2 and 20” fee structure with a hard hurdle rate of 15%. Example of a Hedge Fund Fee StructureĪBC Fund is a hedge fund with $100 million assets under management. For example, if a hedge fund returned 25% with a 10% soft hurdle rate, incentive fees would be collected on the total portfolio return of 25%. SoftĪ soft hurdle rate means that incentive fees are collected on the entire return of the portfolio so long that the return is greater than the hurdle rate. For example, if a hedge fund returned 25% with a 10% hurdle rate, incentive fees would be collected on the excess return of 15%.
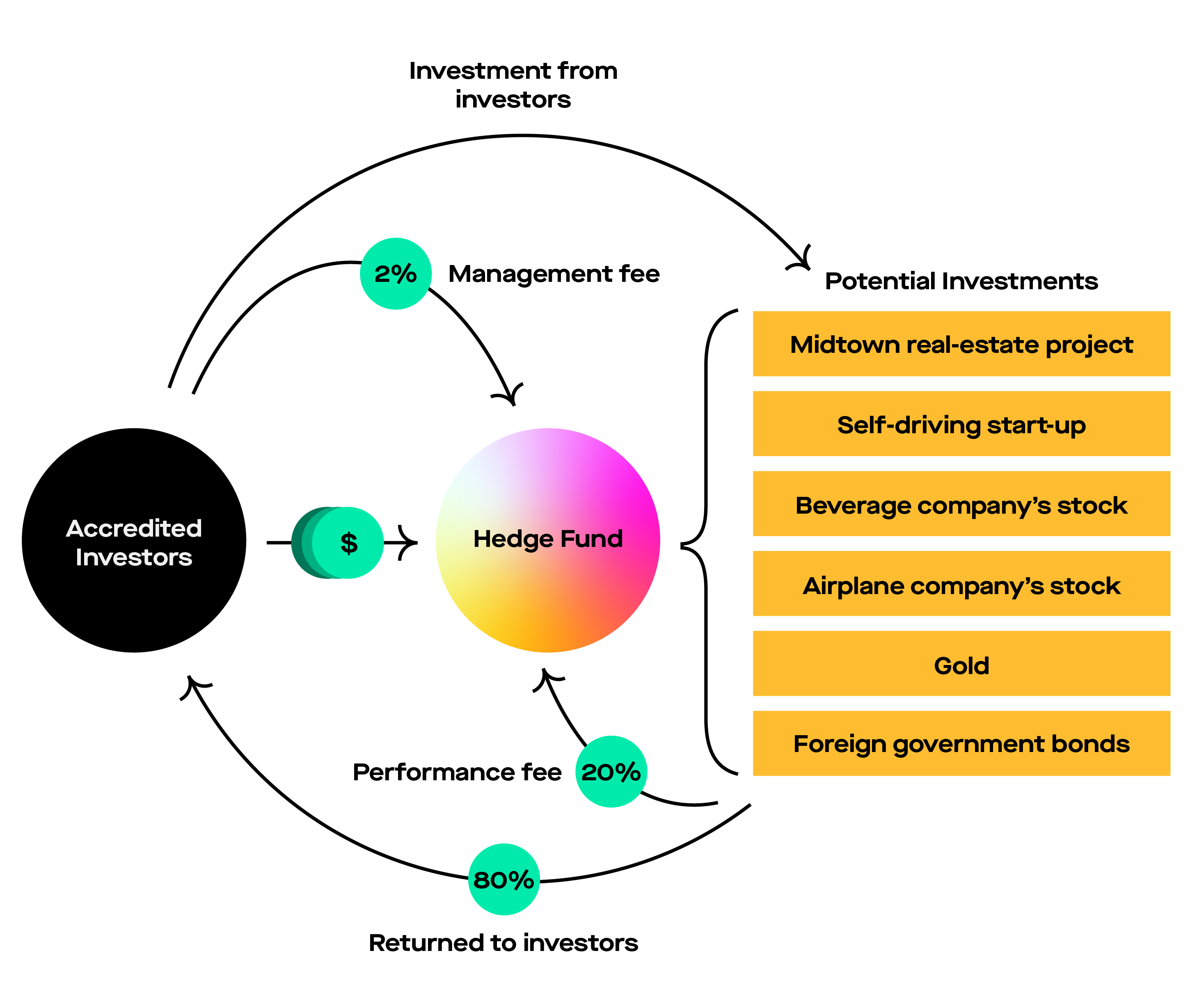
HardĪ hard hurdle rate means that incentive fees are only collected on returns in excess of the benchmark. Incentive fees are only collected when the portfolio generates a higher return than the hurdle rate. It means that the fund manager will charge a 2% management fee applied to the assets under management and a 20% incentive fee on returns greater than a specified hurdle rate. Hedge Fund Fee StructureĪ common hedge fund fee structure is called “ 2 and 20”. Strategies that seek to gain from long and/or short positions in equities and derivatives. Macro strategies revolve around the prediction and projection of macro events. Strategies that seek to gain from global economic events and trends such as interest rate changes, currency changes, political changes, and others, by acquiring holdings with positive or negative exposure to such macro events. Strategies that seek to gain from price discrepancies between related securities whose price discrepancy is expected to be resolved over time. Strategies that seek to gain from inefficient price changes due to specific corporate events, corporate restructurings, mergers and takeovers, asset sales, spin-offs, bankruptcies, and other events. Each strategy entails different risk and reward profiles: 1. identifies four main classifications of hedge fund strategies. Due to the deep pockets of institutional investors, they play a major role in the securities market. Institutional investors include pension funds, mutual fund companies, insurance companies, commercial banks, mutual funds, or hedge funds. Securities and Exchange Commission goes into further detail in defining “accredited investors.”Īn institutional investor is a non-bank individual or company that trades securities on behalf of its members in large dollar or quantity amounts. In the United States, one must have a net worth of at least $1,000,000 (excluding the value of the primary residence) or an annual income of at least $200,000 for the past two years.

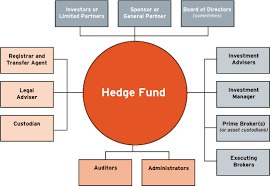
Hedge funds are only accessible to accredited and/or institutional investors.Īn accredited investor is an individual or business entity that is allowed to invest in securities that may not be registered with the financial authorities. The four main classifications of hedge fund strategies are event-driven, relative value, macro, and equity hedge.ĭefining Accredited and Institutional Investors.Hedge funds are only accessible to accredited and/or institutional investors.A hedge fund, an alternative investment vehicle, is a fund that pools investors’ money together and utilizes sophisticated investment strategies to generate returns.Understand any limitations to time restrictions imposed to redeem shares.Understand how a fund's performance is determined and whether it reflects cash or assets received by the fund as opposed to the manager’s estimate of the change in the value.Understand how a fund’s assets are valued as hedge funds may invest in highly illiquid securities and valuations of fund assets will affect the fees that the manager charges.Evaluate potential conflicts of interest disclosed by hedge fund managers and research the background and reputation of the hedge fund managers.Determine if the fund is using leverage or speculative investment techniques which will typically invest both the investors’ capital and the borrowed money to make investments.Understand the level of risk involved in the fund’s investment strategies and that they equate with personal investing goals, time horizons, and risk tolerance.Read the hedge fund’s documents and agreements which contain information about investing in the fund, the strategies of the fund, the location of the fund, and the risks anticipated by the investment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
